Uncover the mystery behind lactose intolerance triggers. Discover the surprising factors that may be causing your discomfort.Do you know?
Table of Contents
Introduction to Lactose Intolerance
If you’ve ever felt funny after eating ice cream or drinking milk, you might have experienced something called lactose intolerance. But what exactly is lactose intolerance, and why is it important for our digestive health?
Lactose intolerance is like having a tummy that doesn’t quite agree with certain foods. It’s when your body has trouble digesting a natural sugar called lactose found in dairy products like milk, ice cream, and cheese. Imagine your tummy as a picky eater that says, “No, thank you,” to these foods because it’s missing something it needs to handle lactose properly.
So, when you hear about lactose intolerance, it’s like knowing why your tummy might not feel happy after enjoying a creamy scoop of ice cream or a cheesy pizza. It’s all about how our bodies work with the foods we eat.
Now, let’s dive deeper into what lactose really is and why it can sometimes cause these tummy troubles.
What Is Lactose?
Let’s talk about lactose, a word you might have heard before when talking about milk and dairy products. Lactose is a type of sugar found in milk and dairy foods, like cheese and yogurt. It gives these foods a slightly sweet taste.
Lactose in Our Daily Foods
You might not realize it, but many of the foods we eat every day contain lactose. Milk, ice cream, butter, and even some breads and cereals have lactose in them. So, if you drink a glass of milk or have a bowl of ice cream, you’re taking in some lactose.
Some people have trouble digesting lactose, which can cause things like stomach aches or bloating. That’s why it’s important to understand what lactose is and how it affects our bodies.
The Role of Lactase in Digesting Lactose
Have you ever wondered why some people have trouble digesting certain foods, like milk or ice cream? It all comes down to a special enzyme called lactase. But what exactly is the role of lactase in digesting lactose? Let’s explore this fascinating process in simpler terms for you to understand.

Image courtesy of www.usdairy.com via Google Images
What Happens When Lactase Is Missing?
Lactase is an enzyme in your body that helps break down lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. When you drink a glass of milk or enjoy a bowl of ice cream, your body needs lactase to break down the lactose into smaller pieces that your body can absorb. However, some people don’t have enough lactase in their bodies, leading to what we call lactase deficiency.
When lactase is missing, the undigested lactose moves into the large intestine instead of being absorbed by the body. This can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms like bloating, gas, stomach cramps, or diarrhea. So, without enough lactase, your body struggles to digest lactose properly, leading to what we know as lactose intolerance.
Identifying Lactose Intolerance
Do you sometimes feel bloated or have tummy troubles after drinking milk or eating ice cream? You might be experiencing lactose intolerance! Let’s explore what this means and how you can figure out if you have it.
Common Symptoms of Lactose Intolerance
When you have lactose intolerance, your body has a hard time digesting a natural sugar called lactose found in dairy products. Some signs to look out for include stomach cramps, bloating, gas, and diarrhea after eating foods like cheese, yogurt, or milkshakes.
If you notice these symptoms happening to you often, especially after eating dairy, it might be a good idea to talk to a doctor. They can help confirm if lactose is the culprit behind your discomfort.
Why People Develop Lactose Intolerance
Have you ever wondered why some people can’t enjoy ice cream or drink milk without feeling sick afterward? It all comes down to something called lactose intolerance.

Image courtesy of www.freepik.com via Google Images
Genetic Factors in Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance can be passed down from your parents through your genes. This means that if someone in your family, like your mom or dad, is lactose intolerant, you might also have a higher chance of being lactose intolerant too. It’s like inheriting traits like eye color or hair texture, but with how your body digests milk sugar.
Changes in Lactase Levels as We Grow
When we’re babies, our bodies produce a lot of an enzyme called lactase that helps break down lactose in milk. But as we get older and start eating more solid foods, our bodies make less lactase because we don’t need as much milk. This decrease in lactase production can lead to lactose intolerance in some people as they grow up.
How Lactose Intolerance Is Diagnosed
So, how do you find out for sure if you’re lactose intolerant? It’s important to know that if you suspect you have lactose intolerance, you need to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Your doctor may suggest a few different ways to figure out if lactose is the culprit behind your tummy troubles.
Special Test Suggestions: One common way doctors diagnose lactose intolerance is through a lactose tolerance test. In this test, you’ll drink a liquid that contains lactose, and then your doctor will measure how well your body breaks it down over time. If your body struggles to digest the lactose, it could be a sign of lactose intolerance.
It’s also possible your doctor may recommend a hydrogen breath test. This test looks for increased levels of hydrogen in your breath, which can happen when undigested lactose ferments in your gut. The results of these tests can help your doctor confirm whether or not you have lactose intolerance.
Living with Lactose Intolerance
Living with lactose intolerance doesn’t mean you have to give up all your favorite treats. With a few changes and some smart choices, you can still enjoy a tasty and satisfying diet.
Lactose-Free Diet Basics
A lactose-free diet means avoiding foods that contain lactose, the sugar found in milk and dairy products. But don’t worry, there are plenty of delicious alternatives to satisfy your cravings. Foods like almond milk, soy yogurt, and dairy-free ice cream can easily replace their lactose-containing counterparts.
| Trigger | Description |
|---|---|
| Dairy Products | Consuming dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt can trigger symptoms of lactose intolerance. |
| Age | Lactose intolerance is more common in adults, as the body produces less lactase enzyme with age. |
| Genetics | Genetic factors can play a role in determining an individual’s ability to digest lactose. |
| Illness or Injury | Suffering from an illness or injury that affects the lining of the small intestine can lead to temporary lactose intolerance. |
Finding Non-Dairy Alternatives
When you’re grocery shopping, keep an eye out for non-dairy alternatives to your favorite dairy products. You can find lactose-free cheese, butter, and even chocolate made from ingredients that won’t upset your tummy. And if you’re feeling adventurous, try coconut milk-based ice cream or oat milk lattes for a tasty change!
The Benefits of Non-Dairy Alternatives
Non-dairy alternatives play a crucial role in maintaining digestive health for individuals with lactose intolerance. When you have lactose intolerance, it means your body struggles to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products like milk and cheese. By opting for non-dairy alternatives, you can still enjoy a variety of tasty foods without experiencing uncomfortable digestive issues.
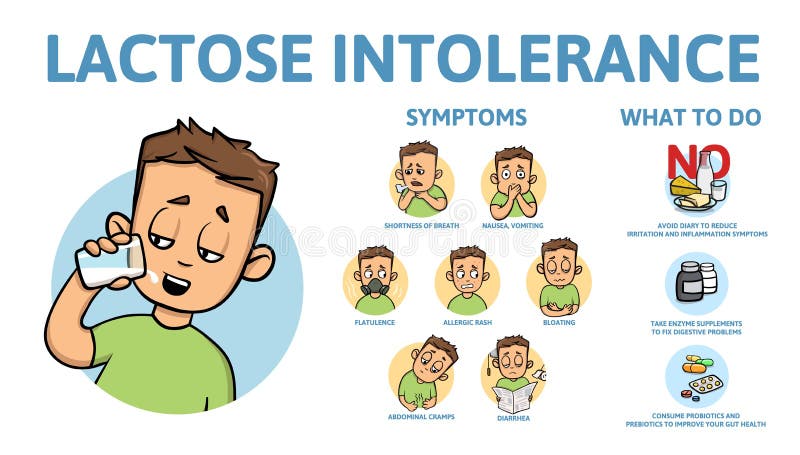
Image courtesy of www.dreamstime.com via Google Images
Finding Non-Dairy Alternatives
Fortunately, there are plenty of delicious non-dairy foods available to replace traditional dairy products. For example, you can try almond milk, coconut milk, or oat milk instead of cow’s milk. These alternatives not only taste great but also provide essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D, just like dairy does.
Exploring different non-dairy options can also add excitement to your meals and snacks. Imagine having a creamy coconut yogurt parfait for breakfast or munching on almond milk ice cream on a hot summer day. Non-dairy alternatives offer a wide range of flavors and textures to suit your tastes.
Tips for Managing Lactose Intolerance
Living with lactose intolerance might seem challenging at first, but with a few simple adjustments, it can be easily managed. Here are some practical tips to help you navigate through your day while dealing with lactose intolerance:
Understanding Food Labels
When shopping for groceries or picking snacks, always check the labels for any hidden lactose. Look for terms like milk, whey, curds, and other dairy derivatives that may indicate the presence of lactose. Opt for products labeled as “lactose-free” or “dairy-free” to ensure you’re making safe choices.
Making Good Food Choices
When dining out or grabbing a meal with friends, don’t hesitate to ask about menu options that are lactose-free. Choose dishes that are less likely to contain dairy, like grilled meats, salads, or vegetable-based entrees. You can also consider bringing your own lactose-free snacks or alternatives in case you’re unsure about available options.
By being mindful of what you eat and making informed choices, you can easily manage your lactose intolerance and enjoy delicious meals without any worries. Remember, it’s all about finding what works best for you and your body!
Conclusion
In conclusion, lactose intolerance is a common digestive issue that occurs when the body has difficulty digesting lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. It can lead to symptoms like stomach aches, bloating, and diarrhea after consuming certain foods.
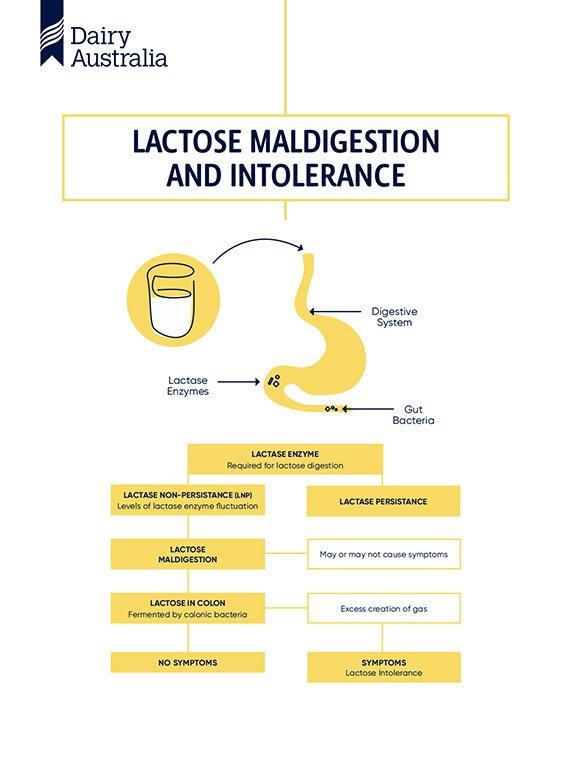
Image courtesy of www.dairyaustralia.com.au via Google Images
Individuals who are lactose intolerant may lack enough of the enzyme lactase, which is needed to break down lactose in the body. This deficiency can be genetic or develop later in life, affecting how dairy products are processed in the digestive system.
Despite the challenges of lactose intolerance, there are various ways to manage the condition and still enjoy a well-balanced diet. This includes following a lactose-free diet, which involves avoiding or limiting dairy products, and experimenting with tasty non-dairy alternatives like almond milk, coconut yogurt, or dairy-free cheese.
By understanding the symptoms, causes, and management strategies for lactose intolerance, individuals can effectively navigate their dietary choices to prevent discomfort and maintain good digestive health. Remember, having lactose intolerance doesn’t mean giving up on delicious foods or missing out on fun–it’s all about making informed decisions and enjoying meals that work best for your body.
FAQs
Will I Have Lactose Intolerance Forever?
If you have lactose intolerance, it’s not necessarily something you’ll have forever. Sometimes, people develop it as they get older, and others find ways to manage it so they can enjoy their favorite foods without any tummy troubles.
Can I Still Eat My Favorite Snacks?
While you may need to make some changes to your diet, you can still enjoy your favorite snacks by choosing lactose-free options or trying yummy non-dairy alternatives. There are plenty of tasty treats out there that won’t upset your stomach.
How Can I Make Sure I’m Choosing the Right Foods?
Reading food labels can be super helpful in making sure you’re avoiding lactose-containing products. Look for terms like “lactose-free” or “dairy-free” to guide you in selecting the right foods. And when you’re out with friends, don’t be afraid to ask about the ingredients in dishes!





