Uncover the surprising link between sugar consumption and genetics in the development of Type 2 Diabetes. Don’t miss out!
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Type 2 Diabetes
- What is Type 2 Diabetes?
- What Affects Your Blood Sugar Levels
- What Role Does Fatty Liver Have?
- The Impact of Pregnancy: Gestational Diabetes
- Lifestyle Choices and Type 2 Diabetes
- Can We Prevent Type 2 Diabetes?
- Treating Type 2 Diabetes
- Summary and Reflections
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Introduction to Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. But what exactly is type 2 diabetes, and why is it important to understand it for our health?
Unlike type 1 diabetes, where the body doesn’t produce insulin, in type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or the cells ignore the insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps sugar from food get into your cells to be used for energy.
When someone has type 2 diabetes, the sugar stays in their blood, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, this can cause serious health problems like heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a health condition that affects how your body processes sugar, also known as glucose. When we eat food, especially ones with carbohydrates like bread or pasta, our bodies break down these sugars into glucose. This glucose is then used as fuel for our cells, giving us the energy we need to run, play, and think.
Definition
In type 2 diabetes, our bodies can’t use the glucose properly. This leads to high levels of sugar in our blood, which can cause serious health problems if not managed correctly. Imagine our bodies as a car that needs gas to run smoothly. With type 2 diabetes, our bodies struggle to effectively use the gas (glucose) we put into them, causing issues in how they function.
Differences from other types
It’s essential to know that type 2 diabetes is different from type 1 diabetes or gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes usually appears in kids and teens and happens when the body can’t produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps our bodies use glucose. Gestational diabetes occurs in pregnant women and can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
What Affects Your Blood Sugar Levels
Our blood sugar levels can be influenced by many factors, including our blood pressure. Let’s take a closer look at how different types of blood pressure can impact our blood sugar.

Image courtesy of www.cdc.gov via Google Images
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. When blood pressure is elevated, it puts a strain on the heart and blood vessels, making it harder for insulin to work effectively in controlling blood sugar levels. This can lead to insulin resistance, a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. Keeping your blood pressure in a healthy range is important for reducing the risk of diabetes.
Low Blood Pressure
On the other hand, low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, can also have implications for blood sugar levels. While low blood pressure itself may not directly cause diabetes, it can be a sign of underlying health issues that may contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. It’s important to monitor blood pressure levels and work with your healthcare provider to maintain a balance that supports overall health and well-being.
What Role Does Fatty Liver Have?
Explanation of Fatty Liver
A fatty liver is a condition where too much fat builds up in the liver cells. It can happen when we eat unhealthy foods, drink too much alcohol, or have certain health conditions.
Link to Diabetes
When someone has a fatty liver, it can make them more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. The extra fat in the liver can make it harder for the body to control blood sugar levels properly. This can lead to insulin resistance, which is a common problem in people with type 2 diabetes.
The Impact of Pregnancy: Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that some women develop during pregnancy. It is important to understand how this condition can affect both the mother and the baby.
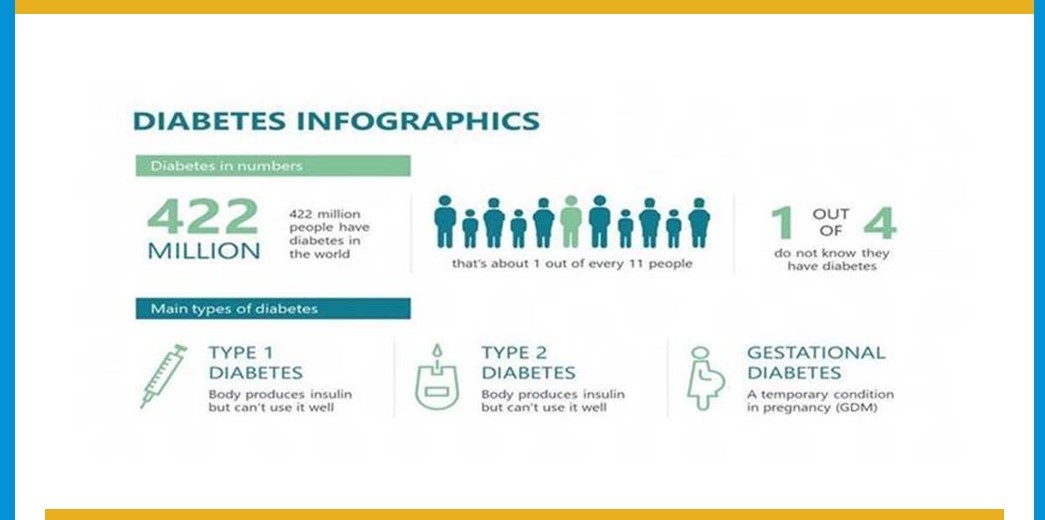
Image courtesy of www.montgomerycountymd.gov via Google Images
Understanding Gestational Diabetes
During pregnancy, the body changes in many ways to support the growing baby. Sometimes, these changes can lead to issues with insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When a pregnant woman’s body cannot produce enough insulin, gestational diabetes can occur.
Connection to Type 2 Diabetes
Women who experience gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. This is why it is crucial to monitor blood sugar levels during pregnancy and after giving birth. By making healthy lifestyle choices, such as eating nutritious foods and staying physically active, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes can be lowered.
The Role of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a super important nutrient that our bodies need to stay healthy. It helps us absorb calcium, which makes our bones strong. You can think of vitamin D like the sunshine vitamin because our bodies can actually make it when we spend time in the sun.
Vitamin D and Blood Sugar Control
When it comes to diabetes, vitamin D might play a part in how our bodies control blood sugar. Some studies suggest that having too little vitamin D could make it harder for our bodies to keep blood sugar levels in check. This could be linked to the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle Choices and Type 2 Diabetes
When it comes to type 2 diabetes, the way you live your life plays a significant role in determining your risk of developing this condition. Making healthy lifestyle choices can help reduce the chances of getting type 2 diabetes, or manage it effectively if you are already diagnosed. Let’s explore how your eating habits and physical activity can impact your risk of type 2 diabetes.
Eating Habits
Your eating habits can have a major impact on your overall health, including your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Foods high in sugar, saturated fats, and processed ingredients can contribute to weight gain, high blood sugar levels, and increased insulin resistance – all factors that can lead to type 2 diabetes.
On the other hand, incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help maintain a healthy weight, stabilize blood sugar levels, and improve insulin sensitivity. By choosing nutrient-dense foods and watching your portion sizes, you can support your body in preventing or managing type 2 diabetes.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining a healthy body and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently, allowing your cells to take up glucose from the blood and control blood sugar levels effectively.
Engaging in activities like walking, running, swimming, or playing sports not only burns calories and helps with weight management but also improves your overall cardiovascular health and boosts insulin sensitivity. By making it a habit to move your body regularly, you can significantly lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and enjoy a host of other health benefits.
Can We Prevent Type 2 Diabetes?
Understanding whether type 2 diabetes can be prevented is essential in taking charge of our health. By making healthy choices, we might lower our risk of developing this condition. Let’s explore some key factors that play a role in preventing type 2 diabetes.
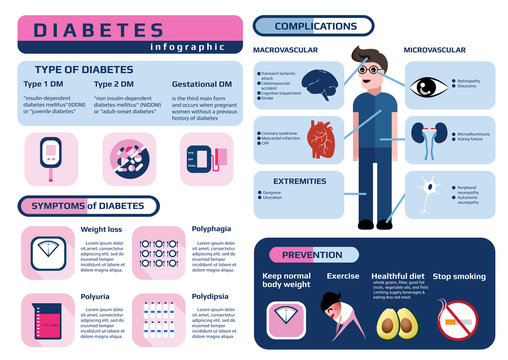
Image courtesy of stock.adobe.com via Google Images
Health Changes
Making changes in our daily habits can significantly impact our risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help keep our blood sugar levels stable. Avoiding sugary drinks and snacks is also important in preventing diabetes. Additionally, staying physically active by engaging in activities like running, playing sports, or dancing can improve our overall health and reduce the likelihood of type 2 diabetes.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Obesity | Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, can increase insulin resistance. |
| Inactivity | Lack of physical activity can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance. |
| Genetics | A family history of type 2 diabetes can increase your risk of developing the disease. |
| Age | Risk increases with age, especially after 45 years old. |
| High Blood Pressure | Hypertension can be a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. |
| High Cholesterol | Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides can increase risk. |
Importance of Early Detection
Detecting any signs or risk factors for type 2 diabetes early on can make a big difference in preventing its development. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help identify any issues that may increase the chances of developing this condition. By staying informed about our health and seeking help when needed, we can take proactive steps to prevent type 2 diabetes before it becomes a concern.
Treating Type 2 Diabetes
When someone is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, their healthcare provider may prescribe medications to help manage the condition. These medications can come in different forms, such as pills or injections, and they work by assisting the body in controlling blood sugar levels. It’s essential to take these medications as directed by the doctor to ensure they are effective in keeping the diabetes under control.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Alongside medications, making lifestyle adjustments plays a vital role in managing type 2 diabetes. One crucial adjustment is maintaining a healthy diet. Eating foods that are high in fiber, low in sugar, and balanced in nutrients can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Physical activity is also crucial. By staying active and incorporating exercise into daily routines, individuals with diabetes can improve their body’s ability to use insulin efficiently and regulate blood sugar levels.
In addition to diet and exercise, managing stress levels and getting enough quality sleep are important aspects of lifestyle adjustments for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Stress and lack of sleep can impact blood sugar levels, so finding ways to relax and ensure proper rest is essential.
Summary and Reflections
After exploring the various factors that contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes, let’s recap some of the key points we discussed.
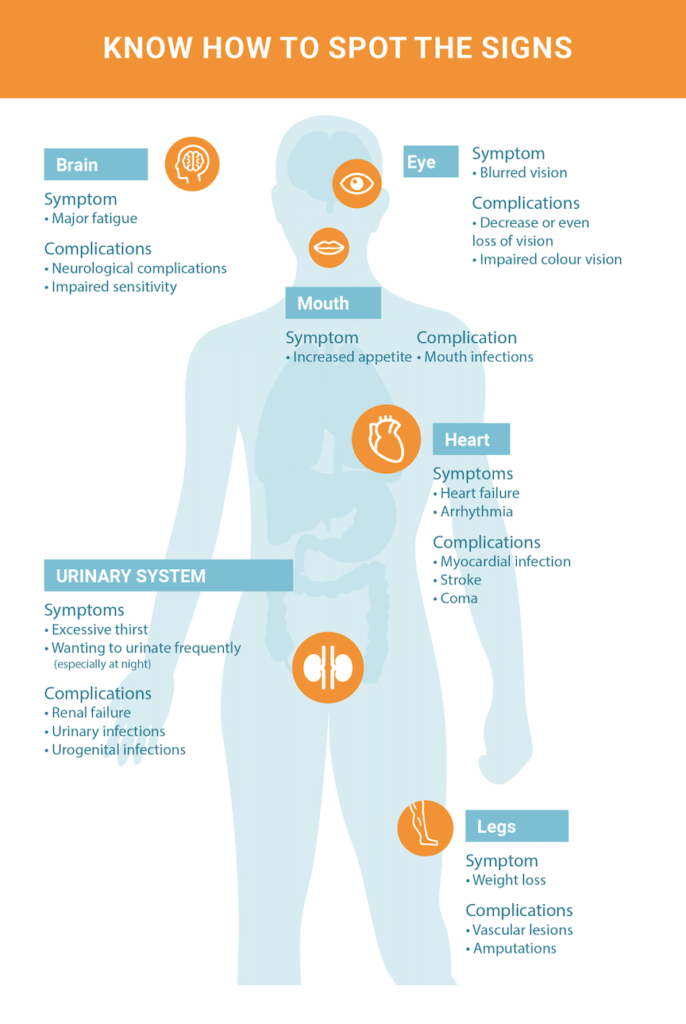
Image courtesy of servier.com via Google Images
Definition
Type 2 diabetes is a health condition that affects how our bodies use glucose, a sugar that gives us energy. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which is often diagnosed in children and requires insulin injections, type 2 diabetes can usually be managed with lifestyle changes.
Differences from Other Types
Type 2 diabetes differs from other types like gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy, and type 1 diabetes, where the body doesn’t make insulin. Understanding these differences can help us recognize the unique aspects of type 2 diabetes.
Affects of High Blood Pressure
Having high blood pressure can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It’s important to keep blood pressure levels in check to reduce this risk and maintain overall health.
Role of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver, a condition where fat builds up in the liver, can be linked to type 2 diabetes. Taking steps to prevent or manage fatty liver can help reduce the chances of developing diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes and Type 2
Gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy, can increase the risk of later developing type 2 diabetes. Monitoring blood sugar levels during and after pregnancy is crucial to managing this risk.
Vitamin D and Diabetes Risk
Vitamin D plays a role in blood sugar control and overall health. Ensuring adequate vitamin D levels through supplements or sunlight exposure may help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle Choices
Healthy eating habits and regular physical activity are key in preventing type 2 diabetes. Making small changes in our lifestyle can have a big impact on our health in the long run.
Prevention and Early Detection
While some risk factors for type 2 diabetes, like high blood pressure and vitamin D deficiency, may be beyond our control, making proactive health changes can help prevent the condition. Early detection through regular check-ups is also essential for managing diabetes effectively.
Treatment Options
Once diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, treatments may include medications to manage blood sugar levels and lifestyle adjustments like diet and exercise. These combined efforts can help individuals live well with diabetes.
By understanding the factors that contribute to type 2 diabetes and taking steps to prevent and manage the condition, we can lead healthier and happier lives. Remember, our choices today impact our well-being tomorrow!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a health condition where the sugar levels in our blood become too high. When this happens, our bodies can’t use the sugar properly, which can lead to health problems.
Can kids get type 2 diabetes?
Yes, kids can get type 2 diabetes too. It used to be more common in adults, but unhealthy eating habits and not enough exercise can also cause kids to develop type 2 diabetes. It’s essential to eat healthy foods and be active to keep our bodies healthy and avoid type 2 diabetes.





