Discover the key to stable health and managing type 2 diabetes with simple yet effective strategies for stable blood sugar.
Table of Contents
Hello readers and welcome to our blog post on managing type 2 diabetes!
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body cannot properly use insulin to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to high blood sugar.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that is characterized by insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels. When the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin, glucose cannot enter cells to be used for energy, resulting in high blood sugar levels. Over time, this can lead to serious health complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. These include genetics, obesity, physical inactivity, poor diet, and factors such as high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels. Individuals with a family history of diabetes are also at higher risk of developing the condition.
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include frequent urination, increased thirst, extreme hunger, fatigue, blurry vision, and slow-healing wounds. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for testing and diagnosis.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing type 2 diabetes involves a series of blood tests to measure blood sugar levels. Treatment for type 2 diabetes typically focuses on managing blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medication, such as insulin and oral medications. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly is crucial for managing diabetes and preventing complications.
Living Well with Type 2 Diabetes
A well-balanced diet is essential for managing type 2 diabetes. Focus on incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals. Limit your intake of sugary beverages, processed foods, and high-fat foods. Consult with a registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| What is Type 2 Diabetes? | Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition where the body is unable to properly use insulin, leading to high levels of glucose in the blood. |
| Causes of Fluctuating Blood Sugar | Unhealthy eating habits, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, genetics, and insulin resistance are common causes of fluctuating blood sugar in type 2 diabetes. |
| Managing Blood Sugar Levels | Regular exercise, a balanced diet, monitoring blood sugar levels, taking prescribed medication, managing stress, and getting enough sleep are key strategies for managing blood sugar levels. |
| The Importance of Stable Blood Sugar | Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential for preventing complications of diabetes such as heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney failure. |
| Seeking Professional Help | It is important to work closely with healthcare providers, including doctors, dietitians, and diabetes educators, to develop a personalized diabetes management plan. |
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise plays a key role in managing type 2 diabetes by helping to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Strength training exercises are also beneficial for building muscle mass and improving overall health.
Medication Management
Medication may be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It is important to take prescribed medications as directed by your healthcare provider and to discuss any concerns or side effects with them. Always follow the recommended dosage and schedule for your medications.
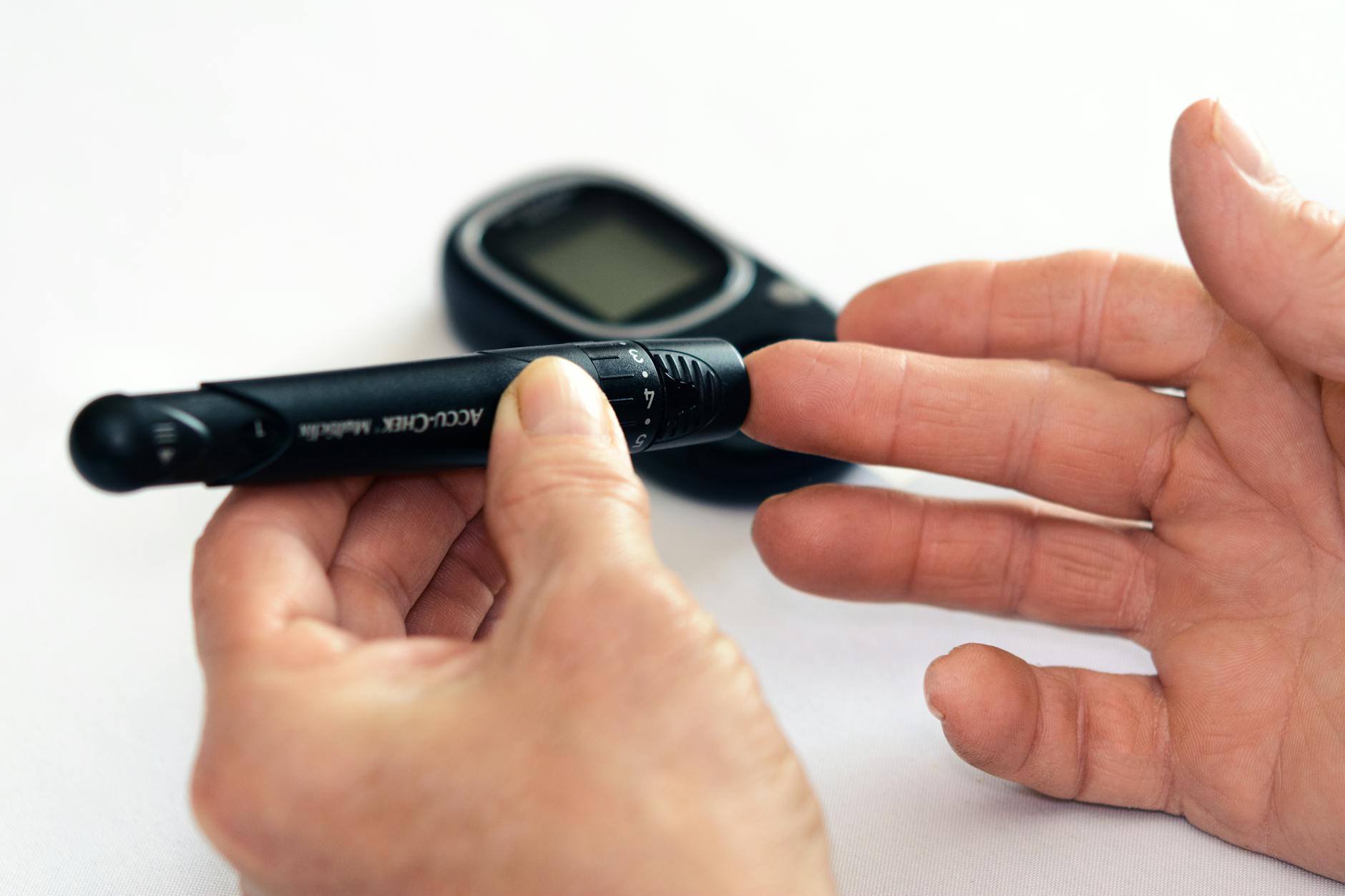
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing type 2 diabetes. By keeping track of your blood sugar levels throughout the day, you can proactively adjust your diet, medication, and activity levels to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Work with your healthcare provider to determine the target range for your blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Managing type 2 diabetes requires a multidisciplinary approach that encompasses lifestyle modifications, medication management, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. By adopting healthy habits, you can take control of your diabetes and reduce the risk of complications. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and guidance on managing your diabetes effectively.
Thank you for reading our blog post on managing type 2 diabetes. We hope you found this information helpful in your journey towards better health and well-being.
FAQ
Can type 2 diabetes be reversed?
While type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition, lifestyle changes such as weight loss, healthy eating, and regular exercise can help manage the condition effectively and even lead to remission in some cases.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
It is recommended to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly, as advised by your healthcare provider. This could range from daily monitoring to periodic checks, depending on your individual health needs.
Are there any specific foods I should avoid with type 2 diabetes?
It is advisable to limit the intake of sugary beverages, processed foods, high-fat foods, and foods high in refined carbohydrates to help manage blood sugar levels effectively. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
How important is physical activity in managing type 2 diabetes?
Physical activity plays a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity, lowering blood sugar levels, and enhancing overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, along with strength training exercises for optimal benefits.