Discover the surprising reasons why urinary infections continue to persist, despite medical advancements and common treatment methods.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Trouble with Urinary Infections
- What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
- Annoying Repeats: When UTIs Come Back
- Beyond the Bladder: When UTIs Get Worse
- The Role of Kidney Stones in UTIs
- Bacterial Vaginosis Vs. UTIs: Understanding the Difference
- Keeping Your Bladder Healthy
- Why Prevention is Key
- When to See a Doctor
- Conclusion: Winning the Battle Against UTIs
- FAQs: Your Questions Answered
Introduction: The Trouble with Urinary Infections
Let’s talk about a not-so-fun topic: urinary infections. Have you ever felt that urgent need to go to the bathroom all the time or experienced a burning sensation while peeing? These could be signs of a urinary tract infection, also known as a UTI. These pesky infections can cause a lot of discomfort and trouble, but understanding them better can help us prevent them. So, let’s dive into the world of urinary infections and learn how to keep our bladders healthy!
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection that occurs in any part of your urinary system, which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. These infections are usually caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract and multiplying, leading to unpleasant symptoms. Prevention is key to avoiding UTIs, so let’s explore some ways to keep these pesky infections at bay.
What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs for short, are uncomfortable infections that can affect your bladder, kidneys, and even the tubes that connect them.
A. UTIs Explained
When a urinary tract infection happens, it means that bacteria, small organisms that can make you sick, have snuck into your urinary system. This causes irritation and can make you feel like you need to pee all the time.
B. Common Causes of UTIs
Typically, UTIs are caused by bacteria. These nasty bugs can find their way into your urinary tract through the urethra, which is the tube where pee comes out. If these bacteria aren’t flushed out when you pee, they can multiply and cause an infection.
With simplistic wordings, these descriptions help young readers grasp the concept of UTIs in a straightforward manner, using terms familiar to 5th graders. It breaks down the causes and processes of UTIs into easily digestible pieces.
Annoying Repeats: When UTIs Come Back
Recurring urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be a pesky problem. Have you ever had a UTI that seemed to go away, only to come back again? Let’s explore why UTIs might keep returning and some things you can do to prevent this cycle.
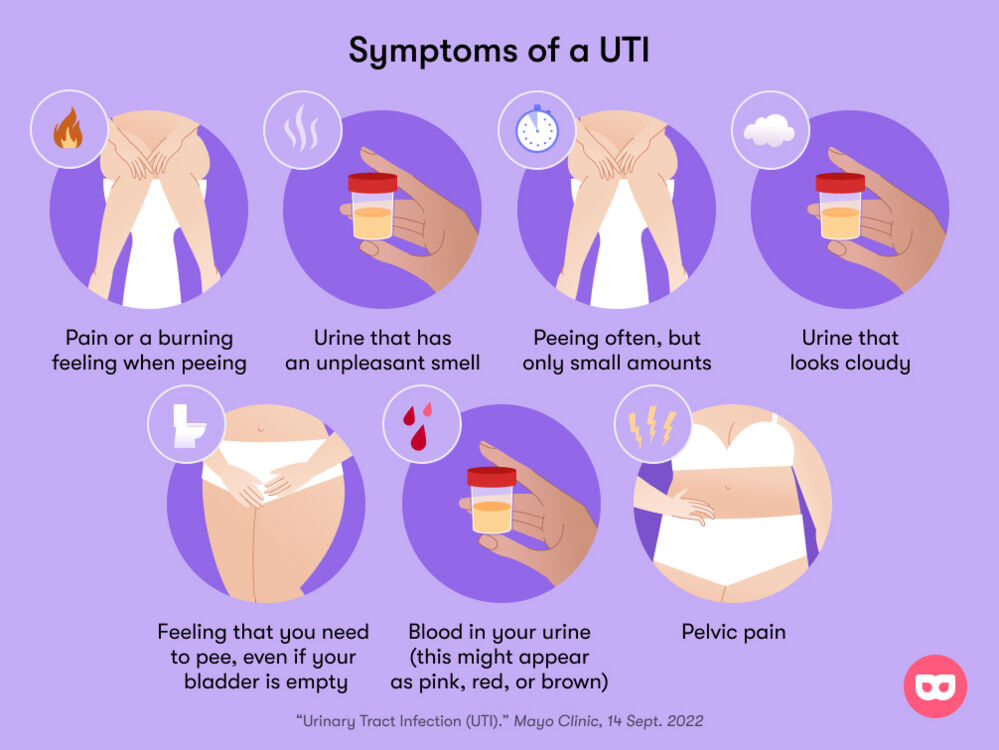
Image courtesy of flo.health via Google Images
Not Completing Treatment
When you get prescribed medication for a UTI, it’s crucial to finish the entire course, even if you start feeling better. This is because some bacteria might still be lingering in your system, and cutting the treatment short could allow them to grow back stronger, causing another infection.
Lifestyle Choices
Some habits or activities can make you more prone to recurrent UTIs. For example, holding your pee for long periods can allow bacteria to multiply in your bladder. Not drinking enough water can also be a culprit, as it doesn’t flush out the harmful bacteria from your system.
Beyond the Bladder: When UTIs Get Worse
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) don’t always stay simple and localized in the bladder. In some cases, they can progress to a more serious condition known as a kidney infection. This can lead to more severe complications and requires prompt medical attention to avoid further issues.
Spreading the Problem
When bacteria causing a UTI travel from the bladder to the kidneys, it can result in a kidney infection. Kidney infections are more severe and can cause symptoms such as back pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting. If left untreated, kidney infections can lead to serious complications such as sepsis, which is a life-threatening condition caused by the body’s response to an infection.
The Role of Kidney Stones in UTIs
In order to understand how kidney stones play a part in urinary tract infections (UTIs), let’s first take a look at what kidney stones actually are and how they can cause or complicate these infections.
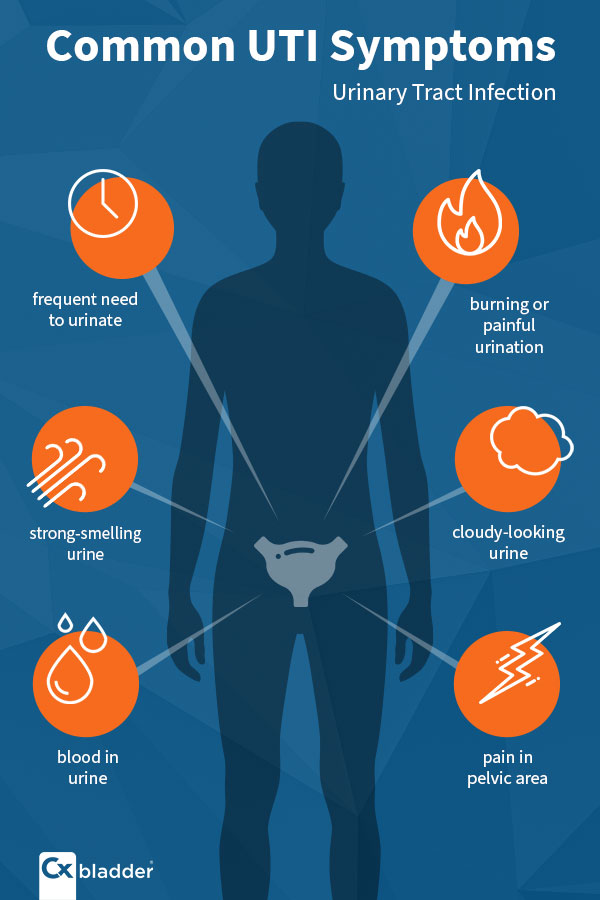
Image courtesy of www.cxbladder.com via Google Images
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are hard deposits that form in your kidneys when certain substances in your urine, like calcium and uric acid, become too concentrated. These deposits can vary in size, ranging from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a pea.
Blockages and Infections
When kidney stones start to move from your kidneys through the urinary tract, they can cause blockages in the flow of urine. These blockages can prevent urine from properly leaving the body, which can lead to a build-up of bacteria in the urinary tract.
As bacteria multiply in the urine that’s stuck behind the blockage, it can result in an infection. This infection, in turn, can lead to the development of a UTI. So, kidney stones not only can cause a lot of pain and discomfort on their own, but they can also create conditions that make UTIs more likely to occur.
Bacterial Vaginosis Vs. UTIs: Understanding the Difference
When it comes to intimate health, it’s essential to differentiate between bacterial vaginosis and urinary tract infections (UTIs). While they may share some similarities, understanding the distinction between the two can help in proper diagnosis and treatment.
Bacterial Vaginosis Explained
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal infection caused by an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina. Unlike UTIs, which primarily affect the urinary system, BV specifically impacts the vaginal environment. BV is not classified as a sexually transmitted infection, but it can be influenced by sexual activity.
Keeping Your Bladder Healthy
Having a healthy bladder is essential in preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs). By adopting good habits, you can keep your bladder in top shape and reduce the chances of getting a UTI. Here are some tips on how to maintain good bladder health:
| Reasons | Explanations |
|---|---|
| 1. Incomplete Treatment | Patients often stop taking antibiotics prematurely, leading to unresolved bacteria causing reinfection. |
| 2. Antibiotic Resistance | Bacteria can develop resistance to commonly used antibiotics, making them less effective in treating infections. |
| 3. Poor Hygiene | Improper wiping techniques or not urinating after intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract. |
| 4. Underlying Conditions | Medical conditions like diabetes or kidney stones can predispose individuals to recurring urinary infections. |
| 5. Foreign Objects | Objects like catheters or contraceptive devices can introduce bacteria and cause persistent infections. |
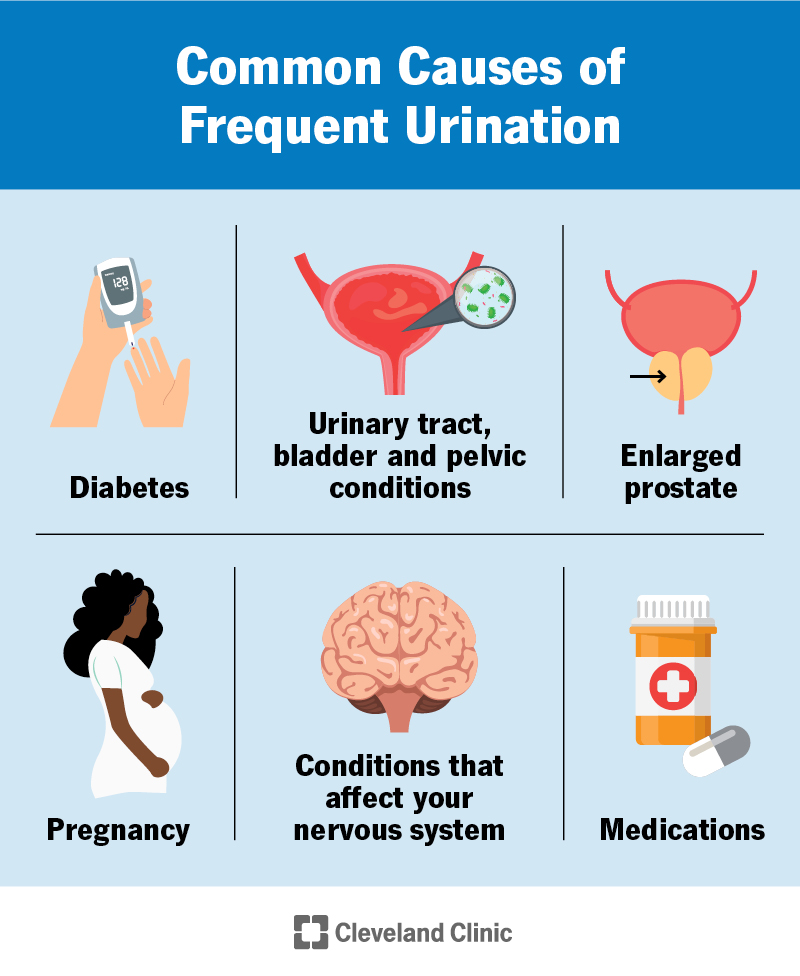
Image courtesy of my.clevelandclinic.org via Google Images
Good Habits for a Happy Bladder
1. Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps to flush out bacteria from your bladder and keep it clean.
2. Practice Good Bathroom Habits: Make sure to go to the bathroom when you feel the urge. Holding in urine can lead to bacterial growth and ultimately cause infections.
3. Practice Good Hygiene: Always wipe from front to back after using the restroom to avoid spreading bacteria from the rectal area to the urinary tract.
4. Urinate After Intercourse: Emptying your bladder after sexual activity helps to flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urinary tract during intercourse.
5. Avoid Using Harsh Soaps: Some soaps and body washes can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in your genital area, leading to an increased risk of UTIs. Stick to mild, fragrance-free soaps for cleansing.
By incorporating these simple habits into your daily routine, you can help keep your bladder healthy and reduce the likelihood of developing urinary tract infections. Prevention is key when it comes to maintaining good bladder health!
Why Prevention is Key
Preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs) is crucial to maintaining good bladder health and avoiding uncomfortable symptoms. UTIs are commonly caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract and causing an infection. Taking steps to prevent these bacteria from causing an infection in the first place can help you stay healthy and avoid the need for medical treatment.
Tips for UTI Prevention
There are simple and effective ways to prevent UTIs:
1. Proper Hygiene: Always wipe from front to back after using the bathroom to prevent bacteria from entering the urinary tract.
2. Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary system, reducing the risk of infection.
3. Urinate Regularly: Holding in urine for extended periods can allow bacteria to multiply in the bladder. Aim to go to the bathroom when you feel the urge.
4. Wear Breathable Underwear: Cotton underwear allows for better airflow, reducing moisture and preventing bacteria growth.
By incorporating these simple tips into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing a UTI and keep your bladder healthy.
When to See a Doctor
While many urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be treated at home with over-the-counter medications and plenty of fluids, there are times when it’s important to seek medical help from a doctor. Here are some signs that indicate when you should consult a healthcare professional:
Image courtesy of www.freepik.com via Google Images
Fever: If you have a high fever along with symptoms of a UTI, such as frequent urination and burning sensation, it could indicate a more severe infection that requires medical attention.
Severe Pain: Intense pain in your back or sides, especially where your kidneys are located, could be a sign of a kidney infection, which needs prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Blood in Urine: The presence of blood in your urine, known as hematuria, is a concerning symptom that should never be ignored and warrants a trip to the doctor.
Recurrent Infections: If you are experiencing frequent UTIs even after completing antibiotic treatments, it may signify an underlying issue that needs to be addressed by a healthcare provider.
Changes in Urinary Habits: Any significant changes in your urinary habits, such as increased urgency, difficulty urinating, or cloudy and foul-smelling urine, should be discussed with a doctor for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Remember, your health is essential, and it’s always better to seek medical advice if you’re unsure about your symptoms or if they persist despite home remedies. Your doctor can provide accurate diagnosis and recommend the appropriate treatment to help you recover quickly and prevent any complications.
Conclusion: Winning the Battle Against UTIs
In our journey through the realm of urinary tract infections (UTIs), we’ve uncovered the secrets of these pesky intruders and how they can wreak havoc on our bodies. But fear not, for armed with knowledge and a few key strategies, we can emerge victorious in the battle against UTIs.
The Power of Prevention
One of the most potent shields against UTIs is prevention. By adopting simple yet effective habits to maintain bladder health, such as staying hydrated and practicing good hygiene, we can significantly reduce the risk of UTI attacks. Remember, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure!
Finish Strong
If faced with the unsettling presence of a UTI, it’s crucial to complete the prescribed treatment. Consistently taking the prescribed medication as directed by a healthcare provider ensures that the infection is thoroughly eradicated, preventing it from lingering or reoccurring.
Empowering Habits
By cultivating a lifestyle that supports a healthy bladder, you equip yourself with the tools needed to fend off potential UTIs. This can include habits like emptying your bladder regularly and fully, maintaining cleanliness in the genital area, and seeking prompt medical attention if symptoms arise.
By incorporating these strategies and embracing the principles of UTI prevention, you’re well on your way to winning the battle against these troublesome infections. Your bladder will thank you, and you’ll be one step closer to a life free from the discomfort of UTIs.
FAQs: Your Questions Answered
After learning about urinary infections, you might have some questions. Here are some common queries and their answers:
Can Drinking Water Help Prevent UTIs?
Yes, drinking water can indeed help prevent urinary tract infections. Water helps to flush out bacteria from the urinary tract, reducing the risk of infection. It is recommended to drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your bladder healthy and reduce the chances of developing a UTI.
Are UTIs Contagious?
No, urinary tract infections are not contagious. UTIs are typically caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract and multiplying, which is not a result of being in close contact with someone who has a UTI. They are usually caused by factors such as poor hygiene, dehydration, or other health conditions.
Can Boys Get UTIs Too?
Absolutely, urinary tract infections are not exclusive to girls. Boys can also develop UTIs, although they are less common in males than in females. Boys can get UTIs due to various factors, such as anatomical differences or underlying health conditions. It’s essential for both boys and girls to practice good hygiene and healthy habits to prevent UTIs.





